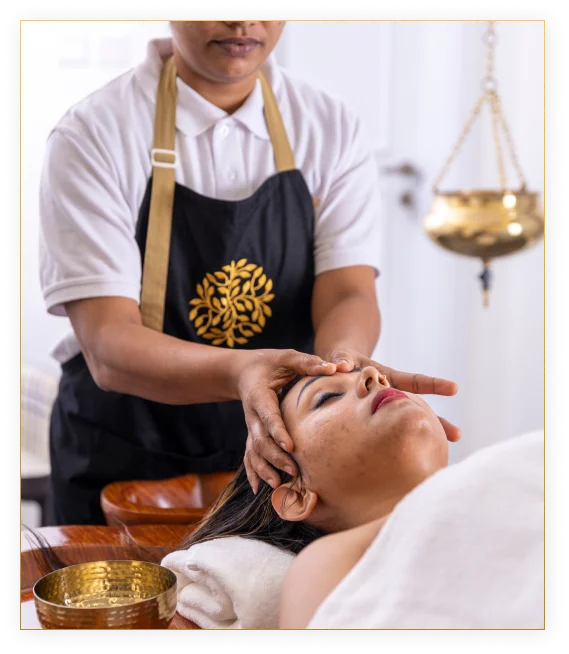
Ayurveda is an ancient science that originated in India thousands of years ago and is practiced still today. It was a by-product of the elements of Indian culture and its quality of absorptive cohesiveness. Ayurveda has not been a part of mainstream Indian culture as has been believed and proposed by many authors and promoters of Ayurveda. The distinct element of Indian culture has been its flexibility to integrate diverse cultural elements and Ayurveda is a complex product of this trait resulting out of assimilation of different cultural strands and medical insights.
In its initial evolution, Ayurveda faced the tension between the competition of superiority of ritual practices versus the scientific use of herbs. What is practiced today is a result of the development of a paradoxically conservative yet progressive culture.